How Are Ceramics Manufactured [7 Simple Steps in 2024]
Time of issue: 2024-12-05 11:13:07
Ceramics are manufactured by shaping raw materials, firing them at high temperatures, and often glazing to create durable, functional products.
Ceramics are an essential part of our everyday lives, from pottery and tiles to high-tech materials used in industries like aerospace and medicine.
Global Reach Ceramic offers Ceramics Products that combine exceptional quality, innovative design that meet the diverse needs of both residential and industrial applications worldwide.
In this article, we will talk about 7 steps on how ceramics are manufactured. Whether you're a beginner, this easy process will give you a clear understanding of how raw materials are transformed into high-quality ceramic products.
What is Ceramic Manufacturing?

Ceramic manufacturing is the process of creating durable, non-metallic products from ceramic materials like clay and other compounds.
While traditional ceramics are often used for artistic or decorative purposes, industrial ceramics are engineered for functionality. These are designed to support machinery, improve manufacturing processes, and deliver high-strength materials for industries such as automotive, aerospace, military, medical, construction, and more.
The process involves shaping and heating natural materials like clay, along with other additives, to create solid, long-lasting products. Ceramic manufacturing produces items that vary widely in size, shape, complexity, and cost, making them essential in both everyday applications and specialized industries.
What Are the Raw Materials of Ceramics?

Ceramics are non-metallic, inorganic materials that are known for their hardness, brittleness, and heat resistance. They’ve been used for centuries to create a variety of products, from everyday items like pottery and bricks to high-tech components in modern industries.
While traditional ceramics were mainly made from clay-based materials, today’s ceramic manufacturing includes a wide range of raw materials depending on the type of ceramic being produced.
Traditional Raw Materials
The foundation of most ceramics, including porcelain, bricks, and stoneware, still lies in natural clay minerals. These clay materials are the key components that give ceramics their ability to be molded into different shapes before firing at high temperatures.
Common clay minerals used in traditional ceramics include:
- Kaolin: A fine, white clay used to make porcelain.
- Ball Clay: A highly plastic clay used for creating detailed shapes.
- Fire Clay: Resistant to high temperatures, ideal for making kiln linings and bricks.
Advanced Ceramics
In addition to traditional materials, advanced ceramics often require more specialized raw materials, particularly chemical compounds that offer superior strength, resistance, and performance. These materials are used in industries like medicine, aerospace, electronics, and defense. Examples include:
- Tungsten Carbide: Known for its hardness and used in industrial machinery and tools.
- Silicon Carbide: Extremely durable and often used in electronics, automotive, and aerospace applications.
Advanced ceramics are also found in high-performance applications such as body armor, providing lightweight but strong protection.
Essential Equipment for Ceramic Manufacturing
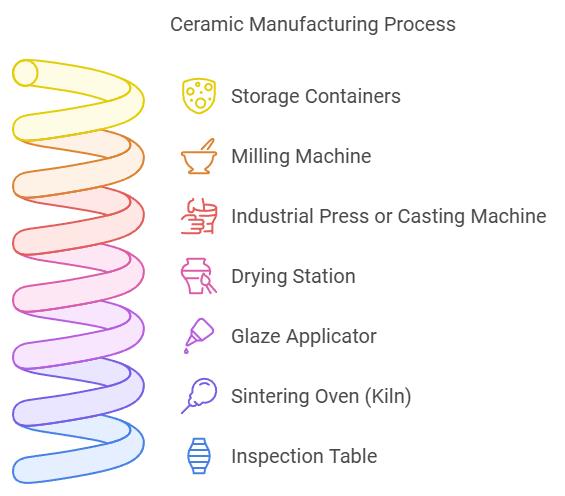
Creating high-quality ceramics requires specialized equipment at every step of the process. Here’s a quick overview of the essential tools that ensure quality and efficiency in ceramic manufacturing.
1. Storage Containers
Raw materials like clay and minerals must be stored in clean containers to prevent contamination, ensuring the final product’s quality.
Next, we’ll prepare these materials for mixing and grinding with a milling machine.
2. Milling Machine
The milling machine grinds raw materials into fine powders, ensuring even mixing and consistency for a smooth ceramic texture.
Next, we shape the materials using an industrial press or casting machine.
3. Industrial Press or Casting Machine
These machines apply pressure or pour materials into molds, shaping ceramics into precise forms, from small parts to large components.
Next, after shaping, the ceramics need drying to prevent cracks, which brings us to the drying station.
4. Drying Station
The drying station removes moisture from shaped ceramics, preventing cracks before they are fired in the kiln.
Next, we apply a glaze for a smooth finish using a glaze applicator.
5. Glaze Applicator
The glaze applicator ensures an even coating of glaze, enhancing both the appearance and durability of the ceramics.
Next, the ceramics are fired in the sintering oven (kiln) to solidify their shape.
6. Sintering Oven (Kiln)
The kiln fires ceramics at high temperatures, hardening and fusing them into durable, finished pieces.
Next, we conduct a final check for defects on the inspection table.
7. Inspection Table
The inspection table is where each piece is carefully examined for defects before being packaged and shipped.
By using these specialized tools, ceramic manufacturers can ensure consistent, high-quality products from start to finish.
How Are Ceramics Manufactured:7 Common Steps 
Ceramic manufacturing is an intricate process that involves several key stages. Each step transforms raw materials into a durable, functional, and often beautiful finished product. Let’s break down these steps to better understand how ceramics come to life.
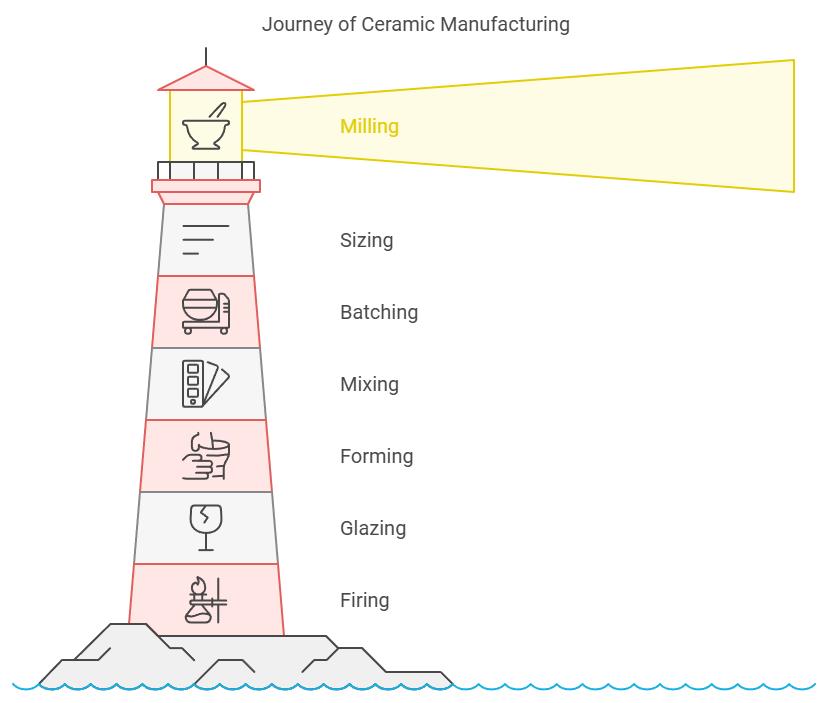
Step #1: Milling
The first step in ceramic manufacturing is milling, where raw materials like clay, minerals, and additives are ground into fine powders. This stage helps remove impurities and ensures the materials are in a form that can be easily mixed and shaped later on. Milling creates a uniform consistency, which is crucial for the final product’s quality.
Next, we move on to sizing, where we’ll control the size of these particles for the best bonding and surface quality.
Step #2: Sizing
In the sizing step, the ground materials are carefully sorted to separate usable parts from the waste. The goal is to ensure the particles are the right size to bond properly and achieve a smooth surface on the final ceramic piece. Proper sizing helps prevent defects and ensures a uniform texture throughout the product.
Next, after sizing, we’ll proceed to batching, where we prepare the materials for the next phase of production.
Step #3: Batching
Batching is the process of weighing and measuring the raw materials before combining them. This step ensures that the right proportions of materials are used for consistency. To keep everything flowing smoothly, vibratory feeders are often used to help maintain a steady flow of materials into the milling machine. Accurate batching guarantees that each batch of ceramic has the same high quality.
Next, once the materials are properly batched, we’ll mix them together to achieve a uniform blend.
Step #4: Mixing
Mixing (or blunging) is the stage where all the raw materials are combined to ensure uniform consistency. This step is critical for achieving a consistent chemical and physical composition throughout the ceramic batch. Pug mills are commonly used for mixing, especially for dry ingredients. The goal here is to make sure that every particle is thoroughly blended, which will help the final product have an even texture and composition.
Next, after the materials are well-mixed, it’s time to form them into their desired shapes.
Step #5: Forming
Forming is where the magic happens—shaping the ceramic into its final form. This can be done through various methods such as slip casting, injection molding, or dry pressing. Traditional ceramics, for instance, might be shaped on a pottery wheel. This stage gives the ceramic its structure, and the method used depends on the product's size, shape, and complexity. Whether it's a decorative vase or a large industrial component, forming shapes the future of the ceramic piece.
Next, after the forming process, we’ll apply glaze to enhance the piece’s appearance and functionality.
Step #6: Glazing
Once the ceramic has been shaped and dried, it’s ready for glazing. Glazing not only enhances the appearance, giving the piece a smooth and shiny finish, but it also improves its durability and functionality. Glaze is typically applied through spraying, which ensures an even coat. The glaze adds color, texture, and a protective layer that helps the ceramic resist damage and enhances its visual appeal.
Next, we’ll take the glazed ceramic and send it to the kiln for firing.
Step #7: Firing
The final step is firing, where the glazed ceramic is placed in a kiln and heated to high temperatures. This intense heat hardens the material, making it stronger and more durable. Firing also fuses the glaze to the ceramic, giving it a smooth, finished surface. This process is essential to make sure the ceramic can withstand everyday use and remain solid for years to come.
Each step builds on the last, ensuring that the raw materials are transformed into a beautifully finished product.
How Are Modern Ceramic Manufactured
Ceramics manufacturing today is more advanced than the traditional methods of the past, such as the simple clay ovens used to fire early pottery. While the fundamental principles remain the same, the process has evolved, especially for industrial ceramics.
Modern ceramics are produced with high precision using methods like molding and casting. Techniques such as injection molding, slip casting, and dry pressing are commonly used in advanced ceramics production.
Injection Molding
Injection molding is a method widely used in the production of advanced ceramics. Similar to plastic molding, this process involves heating ceramic materials until they melt, then injecting the molten substance into molds to create the desired shapes. This technique is efficient and allows for high precision in complex forms.
Slip Casting
Slip casting is a ceramic forming technique ideal for producing intricate shapes that are difficult to achieve on a potter’s wheel. It involves pouring a liquid clay mixture, known as slip, into a plaster mold.
As the slip sets and hardens, it takes the exact shape of the mold. This method is especially useful for creating detailed, uniform ceramics.
Dry Pressing
Dry pressing is a technique that involves compressing ceramic powders inside a mold or die. The loose, granulated powder is compacted under pressure to form a solid shape.
Afterward, the pressed ceramic is fired in a kiln to harden and strengthen the material. This process is often used for producing ceramics that require precise, uniform shapes and sizes.
EndNote
The process of manufacturing ceramics starts with gathering raw materials, which are then carefully processed and mixed to achieve the right blend. Afterward, the materials are shaped into the desired form and go through several stages of heating, including drying, firing, and glazing.
Once these steps are complete, the ceramic product is ready for packaging and use. This detailed process results in high-quality ceramics that are strong, heat-resistant, and versatile.
You can use ceramics in everything from everyday household items to advanced components for industries like aerospace and defense, demonstrating their important role in both daily life and specialized applications.
FAQ
Question: What are the main steps in ceramic manufacturing?
Answer: Ceramic manufacturing involves mixing materials, shaping them, drying, firing, and glazing. These steps create strong, heat-resistant products.
Question: Why is drying important in ceramic manufacturing?
Answer: Drying prevents cracking and ensures uniform moisture content, which is essential for consistent firing and stronger ceramics.
Question: Which industries use ceramics?
Answer: Ceramics are widely used in automotive, aerospace, medical, and construction industries. They provide strength, heat resistance, and durability for various applications.
RECENT POSTS
- Ceramic Cookware vs Cast Iron: What Should You Choose?
2026-01-19
- Ceramic Glazing Techniques & Benefits in 2026
2026-01-19
- The Benefits of Wholesale High-Quality Ceramic Products for Retailers
2025-12-17
- Can You Make an Ashtray with Air Dry Clay? Pros, Cons, and Safer Alternatives
2025-12-17
- The Impact of Ceramic Materials in Energy-Efficient Buildings: Benefits and Applications
2025-12-04
- Top 7 Ceramic Cookware Health Benefits: Why It’s a Safer Choice for Your Kitchen
2025-12-04
- How to Clean Ceramic Planters and Improve Their Lifespan?
2025-11-17
- 15 Best Ceramic Holiday Gift Ideas for 2025: Thoughtful, Elegant & Heartfelt
2025-11-17