What Is The Difference Between Porcelain And Ceramic Jars?
Time of issue: 2024-03-04 11:05:11
When it comes to pottery and ceramics, the terms "porcelain" and "ceramic" are often used interchangeably, leading to confusion regarding their differences. However, delving deeper into their composition, production processes, and properties unveils distinct disparities between the two. In this comprehensive guide, we will elucidate the disparities between porcelain and ceramic jars, shedding light on their unique characteristics, applications, and historical significance.
Understanding Porcelain:
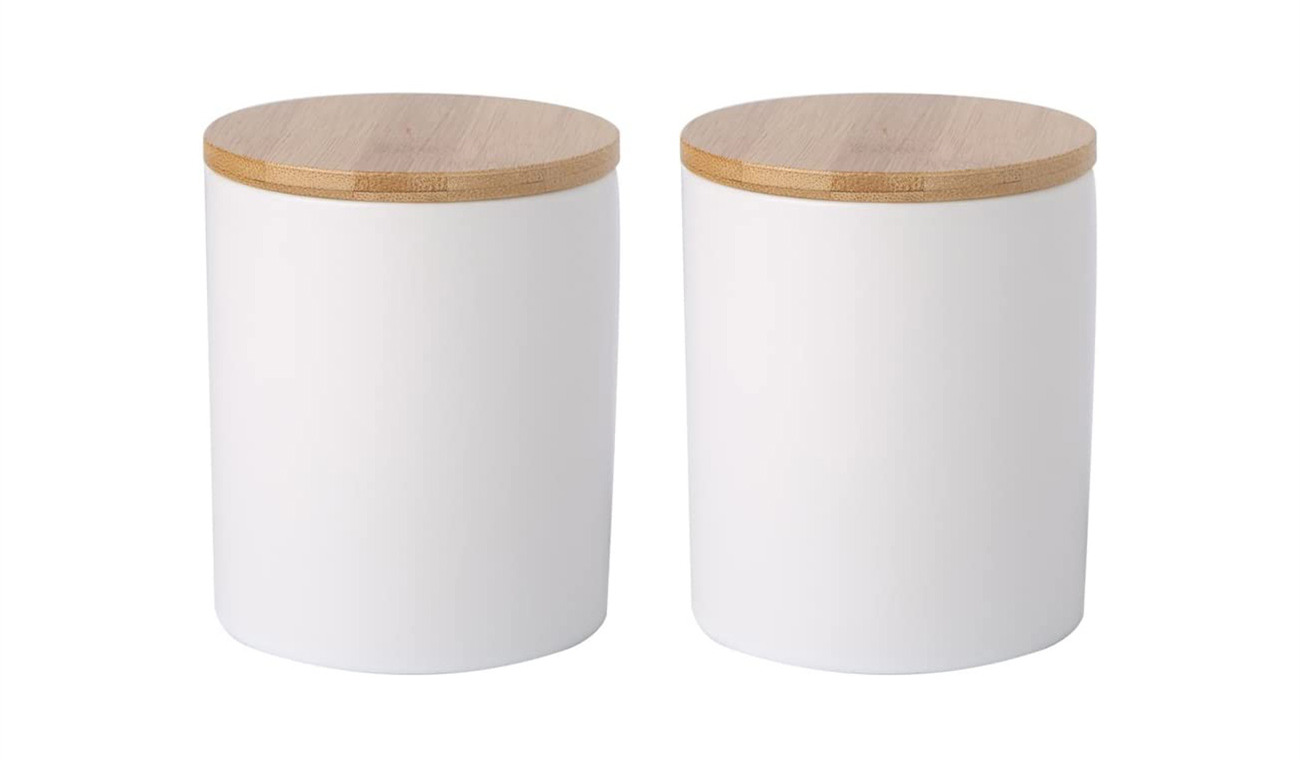

Porcelain, renowned for its elegance and durability, boasts a rich history dating back centuries. Originating in China during the Tang Dynasty (618-907 AD), porcelain quickly gained recognition for its exquisite translucency and superior strength. Traditionally crafted from a combination of kaolin, a fine white clay, and petuntse, a type of feldspathic rock, porcelain undergoes meticulous firing at high temperatures, often exceeding 1,200 degrees Celsius.
The hallmark of porcelain lies in its composition, characterized by a dense, vitrified structure that renders it impermeable to liquids. This imperviousness makes porcelain ideal for storing liquids and preserving contents' freshness, making it a popular choice for jars used in storing delicate substances such as spices, oils, and medicines.
Moreover, porcelain's luminous appearance, often adorned with intricate designs and vibrant glazes, adds a touch of sophistication to any space. Its versatility extends beyond utilitarian purposes, as porcelain jars are prized as collectible art pieces, reflecting cultural influences and artistic innovations across different civilizations.
Exploring Ceramic Jars:
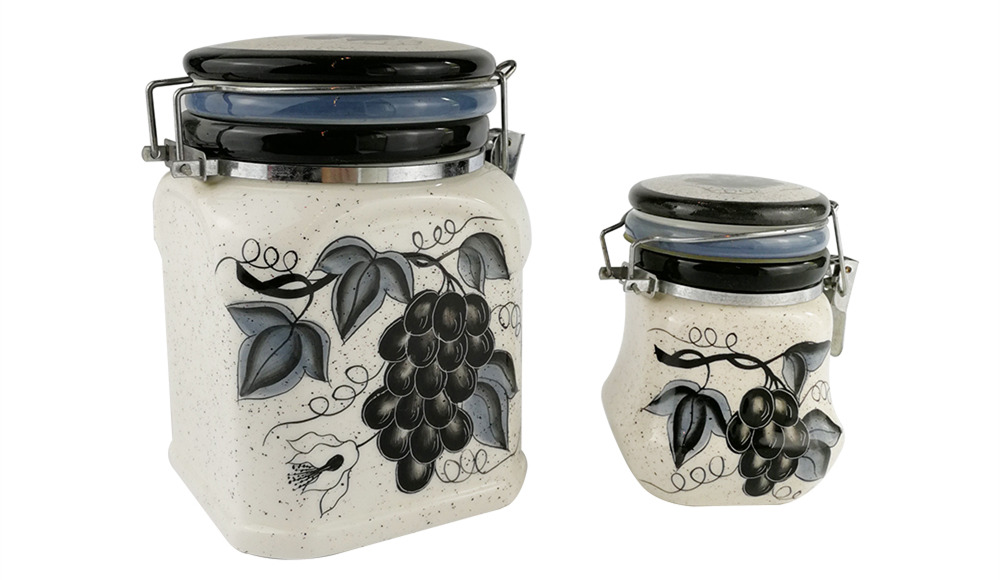

In contrast to porcelain's refined elegance, ceramic jars encompass a broader category of pottery, encompassing various clay-based products fired at lower temperatures. While porcelain represents a subtype of ceramics, ceramics comprise a diverse range of earthenware, stoneware, and terracotta artifacts.
Ceramic jars are crafted from a blend of clay minerals, including kaolinite, illite, and montmorillonite, sourced from diverse geological deposits worldwide. The clay's plasticity and workability allow artisans to mold ceramic vessels into a myriad of shapes and sizes, catering to diverse functional and aesthetic preferences.
Unlike porcelain, ceramic jars undergo firing at temperatures ranging from 600 to 1,200 degrees Celsius, depending on the specific clay composition and desired characteristics. This lower firing temperature results in a porous, slightly permeable structure, making ceramic jars suitable for fermentation, pickling, and other food preservation techniques.
Ceramic jars exhibit a rustic charm, often celebrated for their earthy textures and rustic appeal. They serve as quintessential kitchen essentials, evoking a sense of nostalgia and tradition in modern culinary practices. Additionally, ceramic jars find applications in artistic endeavors, serving as canvases for intricate hand-painted designs and decorative motifs.
Distinguishing Features and Applications:
While porcelain and ceramic jars share commonalities in their clay-based origins, their disparate compositions and properties engender distinct functionalities and applications.
Porcelain jars, prized for their non-porous nature and elegant aesthetics, excel in storing delicate substances susceptible to moisture and air exposure. Their impervious glaze renders them ideal for housing spices, oils, and medicinal compounds, preserving their potency and flavor over extended periods.
On the other hand, ceramic jars, with their porous structure and rustic appeal, find utility in fermenting and pickling applications, allowing for controlled microbial activity and flavor development. Their breathable nature facilitates the exchange of gases during fermentation, ensuring optimal conditions for preserving perishable foods.
Moreover, the cultural and historical significance of porcelain and ceramic jars varies across different regions and epochs. Porcelain, with its origins rooted in ancient China, symbolizes refinement, luxury, and artistic excellence, often associated with imperial patronage and elite consumption. In contrast, ceramic traditions proliferate across diverse civilizations worldwide, reflecting local craftsmanship, indigenous aesthetics, and utilitarian needs.
Conclusion:
In summary, the disparity between porcelain and ceramic jars lies in their composition, production processes, and functional characteristics. While porcelain embodies elegance, durability, and impermeability, ceramic jars exude rustic charm, versatility, and permeability. Understanding these distinctions empowers individuals to make informed choices when selecting jars for culinary, decorative, or collectible purposes, enriching their appreciation for the intricate world of pottery and ceramics.
RECENT POSTS
- Ceramic Cookware vs Cast Iron: What Should You Choose?
2026-01-19
- Ceramic Glazing Techniques & Benefits in 2026
2026-01-19
- The Benefits of Wholesale High-Quality Ceramic Products for Retailers
2025-12-17
- Can You Make an Ashtray with Air Dry Clay? Pros, Cons, and Safer Alternatives
2025-12-17
- The Impact of Ceramic Materials in Energy-Efficient Buildings: Benefits and Applications
2025-12-04
- Top 7 Ceramic Cookware Health Benefits: Why It’s a Safer Choice for Your Kitchen
2025-12-04
- How to Clean Ceramic Planters and Improve Their Lifespan?
2025-11-17
- 15 Best Ceramic Holiday Gift Ideas for 2025: Thoughtful, Elegant & Heartfelt
2025-11-17